Did you know that Google Public DNS servers are completely free and without any registration? Every connection provider is obliged to set up DNS servers for its customers, but it may happen that its service does not suit you, it is slow or even unavailable from time to time, and then pages take a long time to load, or the connection does not work at all. Set Google Public DNS as your DNS server and you’re done. Read here how to… Use Google Public DNS.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Google Public DNS
Google Public DNS is a free, global Domain Name System (DNS) resolution service, that you can use as an alternative to your current DNS provider.
Google Public DNS Free for Everyone
As part of its ongoing efforts to speed up the Internet , Google has decided to open the door to a world of faster connections with the help of its own public DNS resolver, which is called Google Public DNS . What’s more, this invitation to try is so simple it’s almost impossible to resist! Google is now offering its public DNS for free to give you an even faster internet experience.
Most regular Internet users usually don’t have a clue what’s going on with the DNS system because it’s something that is automatically handled by their Internet Service Provider (ISP). We can think of it as a sophisticated Internet control center that translates easy-to-remember domain names, such as www.google.cz , into unique Internet Protocol (IP) numbers, such as 142.251.36.99. These numbers are key for computers on the network to communicate with each other. Although this is an invisible process to most users, we perform hundreds of DNS lookups every day, and some complex websites require multiple DNS queries before loading. This can slow down our internet browsing.
Findings from Google have shown that speed is a key element for internet users. Therefore, over the past months, engineers have been working to improve their public DNS resolver so that users can surf the web even faster, more securely and more reliably. So with Google Public DNS, fast internet is just a click away!
Protection of Personal Data
Google stated that for performance and security purposes, the queried IP address will be deleted after 24-48 hours, but the Internet Service Provider (ISP) and location information is permanently stored on their servers.
In the world of the Internet, there is an invisible network of interconnected paths that allow data to be transmitted and connections to different websites. In the tangled labyrinth of online communication, a public utility plays a key role in helping you reach your desired destinations faster and more efficiently. This tool acts as a guide to your digital journey, guiding you along the optimal routes, thereby enabling a smooth flow of information. It’s like your invisible guide, constantly looking for the best paths for your digital interaction, certainly indispensable in a world where speed and reliability are key factors.
Google's Free Public DNS
Google Public DNS is an excellent Domain Name Server service provided to Internet users worldwide. This innovative service works as a recursive name server and was introduced to the world on December 3, 2009 with the aim of „making the web faster and more secure“. Since then, it has become the largest public service in the world, processing more than a trillion queries per day. The best part? Google Public DNS is not dependent on Google Cloud DNS, which is a hosting service.
As part of its operation, the service offers four IP addresses for recursive name servers, which are mapped to the nearest operation server by anycast routing. However, what’s really interesting is the fact that it doesn’t use traditional DNS nameserver software like BIND. Instead, it relies on a custom implementation that conforms to standards set by the IETF. What’s more, as of March 19, 2013, it fully supports DNSSEC, which means an extra layer of security for users.
One of the reasons for its popularity is its ability to respond correctly to situations where the user enters a non-existent domain name. It responds with a non-existent domain (NXDOMAIN), which is especially important in situations where other DNS providers abuse queries to redirect to advertising sites.
And in terms of security, Google pays attention to protection against various attacks. It documents its cache poisoning resistance efforts, including known attacks like the “ Kaminsky Flaw „, and also actively defends against denial-of-service (DOS) attacks. With this service, your internet experience is not only faster, but also safer.
Innovation and Security: Google Public DNS at the Forefront of Technological Development
Google Public DNS is based on more than a decade of Google's experience and knowledge in networking and technology. It gained its popularity due to its constant efforts to innovate and improve. The service is not only fast and reliable, but also actively participates in the security of user data. To actively protect against various types of attacks and abuses, Google is constantly evolving to provide users with the highest level of security during their online activities.
One of the key elements of success is its transparency and public engagement. The company regularly shares information about its developments, security measures and results, allowing users to monitor and understand how their online environment is protected. This builds trust and provides users with the assurance that they are looking after the security of their internet space.
Overall, Google is a key player in the internet security ecosystem and an effective tool for anyone looking to maximize their online experience. With this leading resolver, you can surf the Internet with the confidence that your connection is fast, reliable and secure.
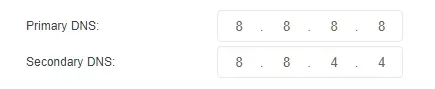
DNS Servers 8.8.8.8

Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Why is Google working on a DNS service?
We believe that a faster and safer DNS infrastructure could significantly improve the web browsing experience. Google Public DNS has made many improvements in the areas of speed, security, and validity of results. We’ve shared these improvements in our documentation, to contribute to an ongoing conversation within the web community.
Q: Can I use Google Public DNS to host my domain name?
Google Public DNS is not an authoritative DNS hosting service and cannot be used as one. If you are looking for a high-volume, programmable, authoritative name server using Google’s infrastructure, try Google’s Cloud DNS.
Q: Does Google Public DNS offer the ability to block or filter out unwanted sites?
Google Public DNS is purely a DNS resolution and caching server; it does not perform any blocking or filtering of any kind, except that it may not resolve certain domains in extraordinary cases if we believe this is necessary to protect Google’s users from security threats. But we believe that blocking functionality is usually best performed by the client. If you are interested in enabling such functionality, you should consider installing a client-side application or browser add-on for this purpose.
Q: Are there any cross-product dependencies with Google Public DNS?
Google Public DNS is an independent service.
Q: Do I need a Google Account to use Google Public DNS?
Use of Google Public DNS does not require any account.
Q: How is Google Public DNS different from my ISP’s DNS service or other open DNS resolvers? How can I tell if it is better?
Open resolvers and your ISP all offer DNS resolution services. We invite you to try Google Public DNS as your primary or secondary DNS resolver along with any other alternate DNS services. There are many things to consider when identifying a DNS resolver that works for you, such as speed, reliability, security, and validity of responses. Unlike Google Public DNS, some ISPs and open resolvers block, filter, or redirect DNS responses for commercial purposes.
Q: How does Google Public DNS handle non-existent domains?
If you issue a query for a domain name that does not exist, Google Public DNS always returns an NXDOMAIN record, as per the DNS protocol standards. The browser should show this response as a DNS error. If, instead, you receive any response other than an error message (for example, you are redirected to another page), this could be the result of the following:
Q: A client-side application such as a browser plug-in is displaying an alternate page for a non-existent domain.
Some ISPs may intercept and replace all NXDOMAIN responses with responses that lead to their own servers. If you are concerned that your ISP is intercepting Google Public DNS requests or responses, you should contact your ISP.
Will Google Public DNS be used to serve ads in the future?
We are committed to preserving the integrity of the DNS protocol. Google Public DNS will never return the address of an ad server for a non-existent domain.
Q: What is DNS over HTTPS (DoH)?
DNS resolution over an encrypted HTTPS connection. DNS over HTTPS greatly enhances privacy and security between a stub resolver and a recursive resolver, and complements DNSSEC to provide end-to-end authenticated DNS lookups.
Use and support
Q: I am using another DNS service now. Can I also use Google Public DNS?
You can set Google Public DNS to be your primary or secondary DNS resolver, along with your current DNS resolver. Please remember that operating systems treat DNS resolvers differently: some prefer your primary DNS resolver and only use the secondary if the primary fails to respond, while others round-robin among each of the resolvers.
If there are differences in security or filtering between configured resolvers, you get the weakest level of security or filtering of all the resolvers. NXDOMAIN filtering or redirection to block pages may work sometimes, but SERVFAIL does not block domains unless all resolvers return SERVFAIL.
Q: Is Google Public DNS suitable for all types of Internet-enabled devices?
Google Public DNS can be used on any standards-compliant network device. If you find any situation where Google Public DNS does not work well, please let us know.
Q: Can I run Google Public DNS on my office computer?
Some offices have private networks that allow you to access domains that you can’t access outside of work. Using Google Public DNS might limit your access to these private domains. Please check your IT department’s policy before using Google Public DNS on your office computer.
Q: In which countries is Google Public DNS available?
It is available to Internet users around the world, though your experience may vary greatly based on your specific location.
Q: Does Google Public DNS work with all ISPs?
Google Public DNS should work with most ISPs, assuming you have access to change your network DNS settings.
Q: Do I need to use both Google Public DNS IP addresses?
You can use Google as your primary service by just using one of the IP addresses. However, be sure not to specify the same address as both primary and secondary servers.
Q: Does it matter in what order I specify the IP addresses?
The order does not matter. Either IP can be your primary or secondary name server.
Q: What is the SLA for the service?
There is no Service Level Agreement (SLA) for the free Google Public DNS service.
Q: I’m running an ISP. Can I redirect my users to Google Public DNS?
ISPs that want to use Google Public DNS should follow the ISP instructions to see if they need to do anything before sending queries to Google Public DNS.
Q: How can I get support from the Google Public DNS team?
We recommend that you join our Google Groups to get useful updates from the team and ask any questions you have. If you are encountering a problem and would like to report it, please see Reporting issues for procedures.
Technical
Q: How does Google Public DNS know where to send my queries?
Anycast routing directs your queries to the closest Google Public DNS server. For more information on anycast routing, see the Wikipedia entry.
Q: Google Public DNS uses Name Server (NS) records published in the DNS root zone and zones of top-level domains to find the names and addresses of the DNS servers that are authoritative for any domain. Some of those name servers also use anycast routing.
Q: Where are your servers currently located?
Google Public DNS servers are available worldwide. There are two answers to this question, one for clients and another for the DNS servers from which Google Public DNS gets the answers it returns to clients.
When clients send queries to Google Public DNS, they are routed to the nearest location advertising the anycast address used (8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4, or one of the IPv6 addresses in 2001:4860:4860::). The specific locations advertising these anycast addresses change due to network conditions and traffic load, and include nearly all of the Core data centers and Edge Points of Presence (PoPs) in the Google Edge Network.
Google Public DNS sends queries to authoritative servers from Core data centers and Google Cloud region locations. Google publishes a list of the IP address ranges Google Public DNS may use to query authoritative DNS servers (not all the ranges in the list are used). You can use it for geo-location of DNS queries lacking EDNS Client Subnet (ECS) data, and to configure ACLs to allow higher query rates from Google Public DNS.
In addition to this FAQ, Google also publishes the list as a DNS „TXT“ record. Google updates both sources weekly with additions, modifications, and removals. Each IP address range entry includes the IATA code for the nearest airport. Automation for GeoIP data or ACLs should get this data via DNS, not by scraping this web page (see below for an example).
Unlocking VDSL Technology: Explore More About High-Speed Internet, Routers, and Modems
If you’re intrigued by the world of VDSL internet connection and its intricacies, then you’re in for a treat. Dive deeper into the topic by exploring our comprehensive article, where we not only demystify VDSL technology but also delve into the nuances of routers and modems. This is your one-stop resource for all things VDSL. Uncover the secrets behind faster internet speeds and better connectivity – perfect for tech enthusiasts and everyday users alike. Don’t miss out, visit article for more insights and in-depth information!
Discussion
As we conclude this exploration of the dynamic world of Marketing, we invite you to share your experiences, insights, and tips in the comments below.
- Have you encountered specific challenges or discovered effective strategies in your journey with digital marketing? We encourage you to contribute to our community by sharing your valuable expertise. If you have questions or seek advice on any aspect related to Marketing, feel free to ask.
Let’s foster a collaborative space where knowledge is shared, questions are answered, and the community thrives. Your input can be instrumental in helping others navigate the nuances of Digital marketing and unlock new levels of success in the realm of online marketing.









